What is a Core Board?
Embedded core boards, also known as SOM (Systems-on-Module) boards, integrate the CPU and various peripherals such as memory (DDR), storage (eMMC or FLASH), power management (PMIC), and oscillators. They also provide interfaces like USB, GPIO, SPI, I2C, UART, Ethernet, PCIe, etc., to meet the needs of various applications.
Core boards are typically connected to the baseboard using board-to-board connectors, stamp holes, gold fingers, COM Express, and other forms, and usually bring out all or most of the CPU's functional pins. Users only need to design the functional interface circuitry according to the application scenario when designing a product, which reduces the difficulty of hardware development and saves development time.
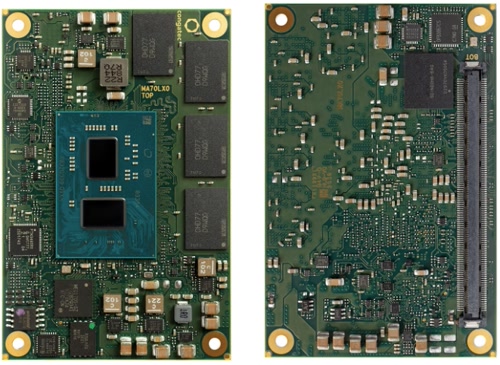
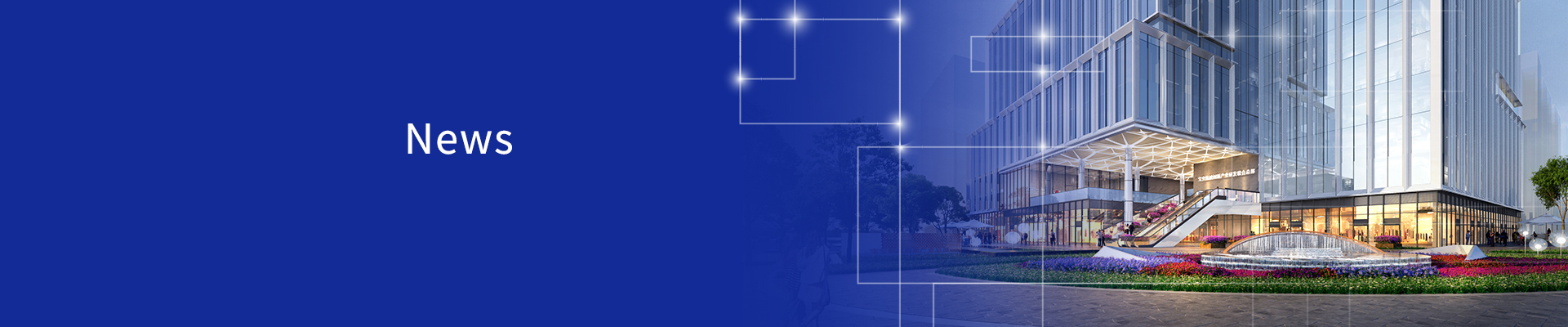
Intel Atom x6000E COM Express core board
Source: Congatec
SOMs are suitable for a variety of industries including industrial automation, medical devices, automotive electronics, communication systems, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Using SOMs can greatly shorten the product development cycle, reduce overall costs, and improve product reliability.
Classification of Core Boards
To ensure the compatibility, modularity, and scalability of embedded core boards in terms of hardware and software, multiple standards have been defined by different organizations or companies. Common embedded core board standards are as follows:
Open Standard Module (OSM)
The OSM core board is a solderable LGA package module with a compact size, the largest being 45mm x 45mm, and the module power is usually below 15W. It is very friendly for IoT applications and can meet the growing performance needs at a low cost.

OSM standard IMX8MP core board
Source: ADLINK
QSeven (Q7)
A standard for embedded processor modules based on the ARM architecture introduced by NXP Semiconductors (formerly Freescale Semiconductor). The standard uses a 230-pin MXM gold finger design for high-speed I/O connections in handheld devices, HMI, and signage applications.
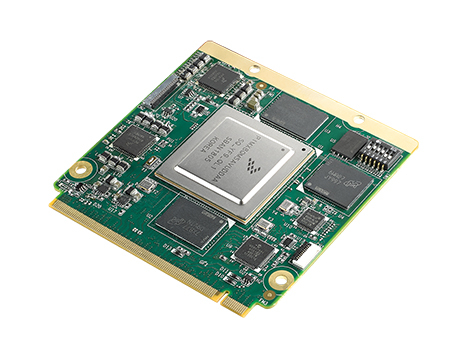
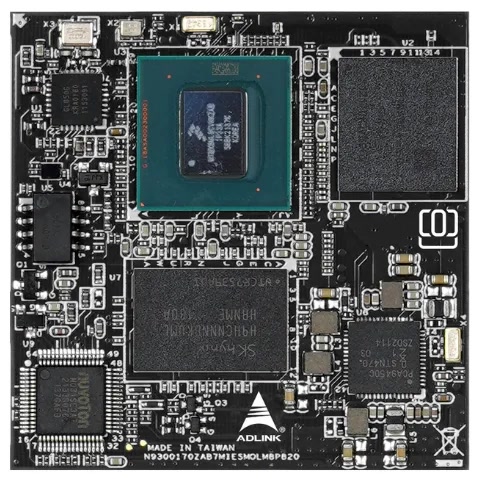
NXP i.MX 8QM Qseven core board
Source: Advantech
SMARC
SMARC (Standard Module Advanced RISC Computer) is an open standard for defining embedded computer modules based on the ARM architecture. It uses a 314-pin MXM gold finger connector and is suitable for products requiring high performance and low power consumption.

Intel Atom x7000 series (Amston Lake) core board
Source: ADLINK
COM Express
A modular computer standard defined by PICMG (PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group) that supports various processor architectures such as x86, ARM, and PowerPC. COM Express modules come in three sizes: Mini, Basic, and Compact, which can be chosen according to specific applications and power requirements.
To adapt to the next generation of AIoT applications, COM Express R3.1 has added support for multiple advanced interfaces, including new PCIe Gen 4 interfaces for Type 6/7/10, USB 4.0 interfaces for Type 6 modules, a second PCIe Clock for Type 7 modules, and upgrading 10G Ethernet to support CEI sideband signals.

COM Express Type 6 11th Generation Intel Core i7 core board
Source: ADLINK
Embedded Core Board PCB Design Guide
With the increasing performance of embedded processors and faster memory speeds, the number of layers in embedded core boards has evolved from the early 4 layers to 8-12 layers. Due to the support for more high-speed interfaces, the requirements for material loss have also increased.
The general steps for designing the PCB of an embedded core board are as follows:
Determine Component Layout
Generally, the core board standard has specified the standard shape and interfaces, and the layout of the components will not change much. The general approach is to follow the CPU reference manual requirements, adhere to the best fanout layout design, determine the layout of the CPU, DDR, and Flash, and then optimize the layout of the power supply and surrounding components.
Determine Board Thickness
Conventional PCB finished thicknesses are 0.5mm, 0.8mm, 1.0mm, 1.2mm, 1.6mm, 2.0mm, 3.2mm, 6.4mm, etc. Generally, the core board design standard will specify the board thickness, and the design should follow the corresponding requirements. If there are no specified requirements, it can be made thicker from the perspective of structural reliability.
Determine PCB Layers and Divide Functional Layers
Determine the total number of layers and divide the signal layers, power layers, and ground layers. This needs to be considered comprehensively from a systematic perspective and is a result of mutual compromise. First, the number of layers must meet the wiring requirements, then meet the wiring requirements of high-speed signal lines, and finally consider the requirements for power integrity, EMC, and thermal design. Under the premise of meeting the functions, try to reduce the number of PCB layers as much as possible.
Determine Inner and Outer Layer Copper Thickness
When designing the stack, the thickness of the copper foil must be balanced so that the thickness of the power/ground plane layer copper meets the current carrying requirements. Copper thickness above 3oz is considered thick copper and is commonly used for high voltage and high current power electronic products.
For the thickness of the copper on the signal layer, the line width/spacing is small, and the copper needs to be as thin as possible to meet the precise etching requirements. High-speed signal lines, due to the skin effect, have current flowing only near the surface of the copper foil, and thicker copper foil will not bring better performance. Therefore, the copper thickness of the inner signal layer is usually Hoz, that is, 0.5 ounces.
Determine the Distribution of Impedance Lines
The high-speed interface signal lines on the core board all have impedance requirements, common ones being single-ended 50Ω and differential 100Ω, etc. Impedance control requires a reference plane, and the copper thickness, dielectric constant, line width, and line spacing of the wiring will all affect the impedance. When designing impedance lines, try to reduce the number of layers where impedance lines appear under the premise of meeting the impedance requirements.
EDA tools all support impedance calculation, and the parameters of the wiring can be adjusted according to the designed stack structure.
Determine Via Structure
Most core boards, due to their high-density properties, use blind and buried vias to optimize wiring space. Blind and buried vias also cause the PCB to need multiple pressings, increasing the process and manufacturing difficulty of the PCB, thus making it more expensive.
When designing the stack, try to simplify the structure of the holes under the premise of meeting the design requirements.
Select the Substrate, PP, and Copper Foil that Meet the Design Requirements
FR-4 can meet the needs of most PCBs, is cheap, and has good electrical performance. High-speed PCBs will use high-speed substrates, such as Panasonic's Megtron4/6, etc. High-speed PCBs need to choose dielectric materials with the lowest loss tangent and smaller dielectric constant to meet the loss requirements of high-speed signals.
The roughness of the copper foil (copper teeth) makes the width and spacing of the lines uneven, leading to uncontrollable impedance, and due to the skin effect, the current is concentrated on the surface of the conductor, and the surface roughness of the copper foil affects the length of the signal transmission. When the signal frequency is below 5GHz, the effect of copper foil roughness is not very obvious, and it begins to increase when it is greater than 5GHz. It needs to be paid more attention to in the design of high-speed signals greater than 10GHz.





