Why Use Press-Fit Assembly Technology?
The Press-Fit process is a solderless connection technology that uses mechanical pressure to insert press-fit compatible connector pins into PCB press-fit holes. The pins, which have expansion capabilities, form tight contact with the metallized hole walls in the press-fit holes, thereby achieving electrical connection. The cross-sectional dimensions of pin connectors are typically larger than the diameter of PCB metallized holes to ensure tight fit during the press-fit process.
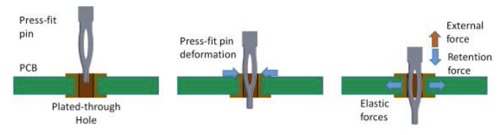
Press-Fit Process
Source: onsemi
Advantages of Press-Fit Assembly Technology:
Press-fit technology can provide stable and reliable electrical connections, especially in high-speed and high-frequency equipment where it has extensive applications.
No heating is required during the press-fit process, so no thermal stress is generated on PCBs and components, which helps protect sensitive components and PCBs.
Avoids common problems in soldering processes such as cold soldering, short circuits, and poor solder penetration, improving connection reliability and stability.
Under certain number of cycles, press-fit connectors can be repeatedly assembled and disassembled, improving product maintainability and flexibility.
Press-fit technology can reduce rework and defect rates in production, improve overall production efficiency, and simultaneously reduce production costs.
The press-fit process is suitable for automated production lines, improving production efficiency and product consistency.
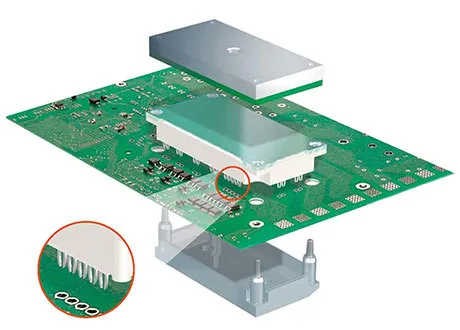
IGBT Module Assembled with Press-Fit Technology
Source: Infineon
Press-fit assembly technology is widely used in automotive, communications, computers, automation equipment, and many other fields. Although press-fit technology has many advantages, it also has limitations, such as high requirements for contact resistance and long-term stability, and the need for specific tools and equipment during press-fit. Therefore, comprehensive consideration based on requirements and costs is needed.
PCB Press-Fit Hole Processing Requirements
PCB press-fit hole processing requirements involve multiple aspects, and strict control of processing requirements is needed to ensure connectors can be correctly installed and electrical connections are reliable.
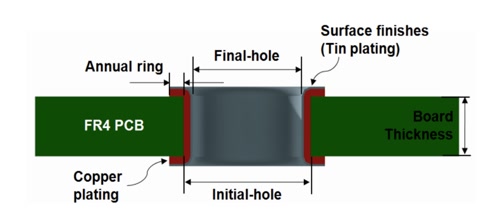
PCB Press-Fit Hole Cross-Section
Source: onsemi
Hole Diameter Size: The diameter of press-fit holes needs to be determined based on component pin dimensions and press-fit technology requirements. Connector specification sheets will provide recommended hole diameters, generally slightly larger than pin diameters.
Hole Diameter Tolerance: Press-fit hole diameter tolerances are stricter than general hole diameter tolerances. Conventional press-fit hole tolerance is ±0.05mm, and strict ones can even reach ±0.025mm.
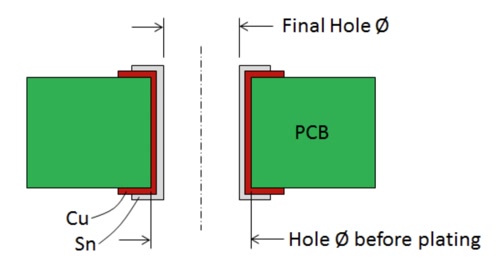
Finished Hole Diameter
Source: onsemi
Plating Requirements: The plating should be uniform, without burrs, with qualified hole copper thickness, and peel strength not less than 120N.
Hole Position Accuracy: Hole positions need to be precise to ensure pins can be correctly aligned and inserted into holes. Position tolerances are usually determined according to IPC standards or customer requirements.
Surface Treatment: Both hole walls and surfaces of press-fit holes undergo surface treatment processes, such as ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) or immersion tin. Generally, press-fit hole specification sheets will specify corresponding surface treatment processes.
Cleanliness: No residues or contaminants should be present inside press-fit holes, as this will affect pin insertion and contact quality.




